








Instruments For Testing Your Innovations


Battery simulator, sometime is called battery emulator, is a very important equipment for testing battery chargers and battery-
To simulate a battery, a power supply emulates many of the battery’s characteristics. The most important characteristic is the ability to sink current when the battery simulator is charged. The battery charger drives charging current into a simulated battery. Therefore, the current is flowing into the simulator power supply. At the same time the simulator must able to source current seamlessly. In fact it must be able to transition between sink and source current without any glitches, even at high speed.
TS250/TS200 Battery Simulator/Emulator
The TS250 and the TS200 modulated power supply can mimic sink and source current the same way a real battery does. They feature a DC OFFSET knob that can adjust the voltage to emulate battery voltage changes. It’s especially useful for simulating a battery for charger circuit testing.
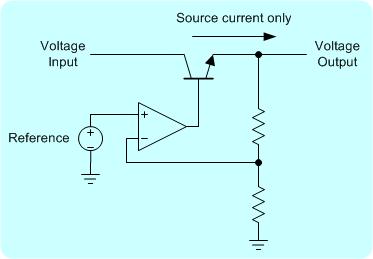
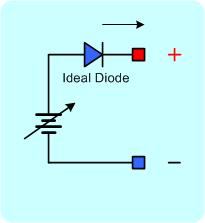
Figure 1. A) Simplified conventional power supply circuit. B) Equivalent circuit.
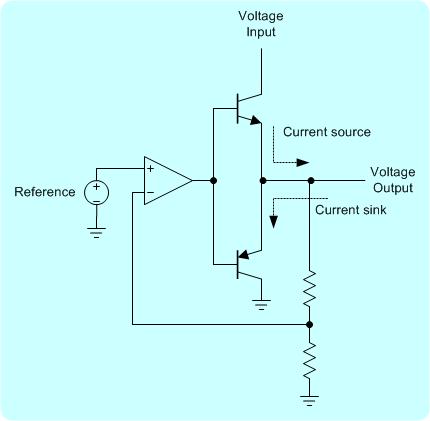
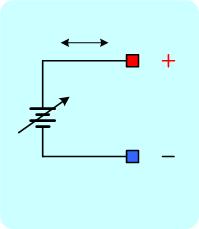
Figure 2. A) Simplified battery simulator circuit. B) Equivalent circuit.
Battery Emulator Applications
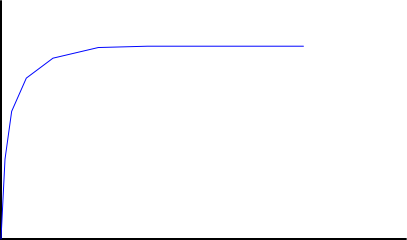


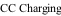



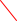
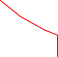


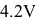
Figure 6. Lithium ion battery CC/CV charging profile.
Selecting a Simulator
Both the TS250 and the TS200 can simulate batteries. The TS250 has an additional feature for output current LCD display. Thus, it eliminates the need for external current monitor. Use the below table for selecting a simulator power supply.
|
Model |
Voltage Range |
Lithium Ion |
NiMH/NiCd |
Alkaline |
Lead- |
|
TS250- |
- |
1- |
1- |
1- |
6V or 12V |
|
TS250- |
- |
1- |
1- |
1- |
6V/12V/24V |
|
TS250- |
- |
1- |
1- |
1- |
6V/12V/24V |
|
TS200- |
0 to +15V |
1- |
1- |
1- |
6V or 12V |
Conventional power supply can only source current, but cannot sink current. Thus a conventional power supply cannot effectively simulate a battery. Figure 1 and 2 show simplified diagrams for the difference between a conventional power supply circuit and a battery simulator power supply. Conventional power supply circuit is depicted with a single NPN transistor allowing current to flow only in one direction – sourcing current. On the other hand, the simulator power supply can sink and source current as shown in Figure 2A. The top NPN transistor is for sourcing current and the bottom PNP transistor is for sinking current.
A simulator can easily change the “battery” voltage by adjusting a knob, compared to a real battery whose voltage is slowly changed by charging or discharging. Thus a battery simulator test equipment is very useful for testing battery-
Battery Simulator Power Supply
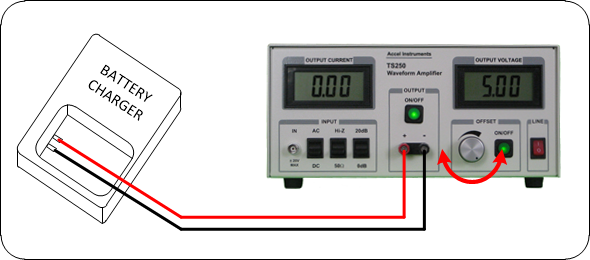
Figure 3 shows a typical battery simulator test equipment connection for testing chargers.
Infinite Capacity
A real battery has a finite capacity. When a battery is charged or discharged, its voltage is changing slowly. On the other hand, the battery emulator keeps its voltage constant. This is equivalent to a battery with infinite capacity or a very large battery. Battery simulator power supply with non-
Simulate Source Impedance and ESR
A real battery has its own internal impedances called ESR (electric static resistance). When current is draw from the battery, its voltage drops slightly. ESR is calculated by the voltage drop (delta voltage) divided by the current. Figure 4 shows a simplified model of a battery ESR. Figure 5 shows how the battery simulator can add ESR to emulate a real battery. Typical ESR is the range of 0.1 ohm to 1 ohm and depends on the battery chemistry, capacity, temperature, age, and state of charge. The TS200/TS250 battery emulators have a very low output ESR, in the range of 0.05 ohm to 0.1 ohm. Add an external series resistor will simulate the ESR. Don't forget to account for connection wire resistance and contact resistance.
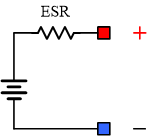
Figure 4. Real battery with internal ESR resistance.
Figure 5. Add an external series resistor to emulate battery ESR.
Battery Charger Testing
Most portable electronic devices have built-
Lithium Ion Battery Simulator and Testing
Battery emulator/simulator is often used to test the charger’s operation over the entire battery voltage range (e.g. 0V to 4.2V). For example, a lithium-
Battery Emulator Advantages
Normally, it takes several hours to fully charge a real battery. For testing purpose, instead of waiting for the charger to charge a real battery, you can use a battery emulator to quickly vary the voltage to emulate the battery being charged. At the same time, you can observe and test the charger behavior to ensure it meets all of the specifications and safely charges the battery. Battery emulator power supply is important for charger circuit testing.
For example, lithium ion battery typically employed a CC/CV (constant-
Multiple-Cell Battery Emulation
Another fundamental use of battery simulator/emulator is to emulate a series connected battery cells inside a battery pack. Various medium-
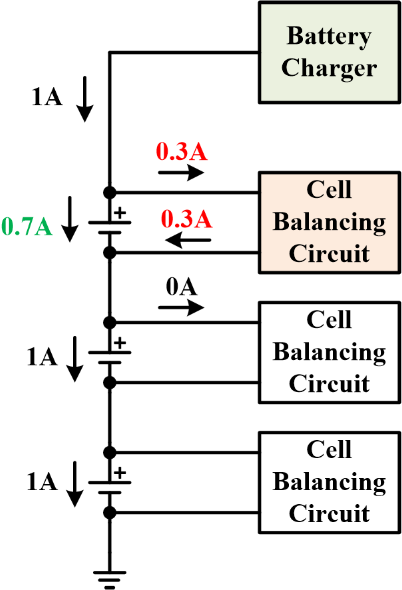
To understand how battery cell balancing work, refer to Figure 7. When one of the batteries approaches being fully charged, the active cell-
Figure 7. Cell balancing circuit divert current away from nearly-
Battery Simulator





Click on the image to enlarge
The charger and the balancing circuitry must to be completely tested throughout the entire design phase. To test the charger and cell balancing circuit design, use a battery simulator(s) to vary the voltage to emulate the cell voltage change. At least one battery simulator is necessary for verifying the cell balancing circuit, preferably use one emulator for each simulated cell. System test engineers can replicate a range of scenarios where the battery is out-
The TS250/TS200 can act as cell simulator for testing cell-
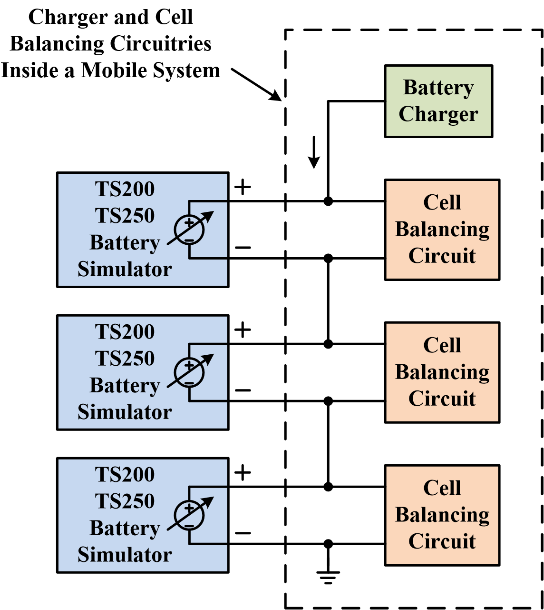
Figure 8. Battery simulators use to test charger and balancing circuit design.

Related Technical Information



Quick Links

Copyright: Battery Simulator

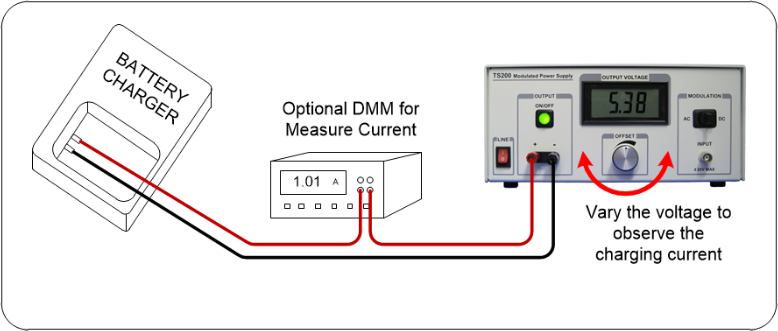
Figure 9. TS200-